- On sale!
- -20%
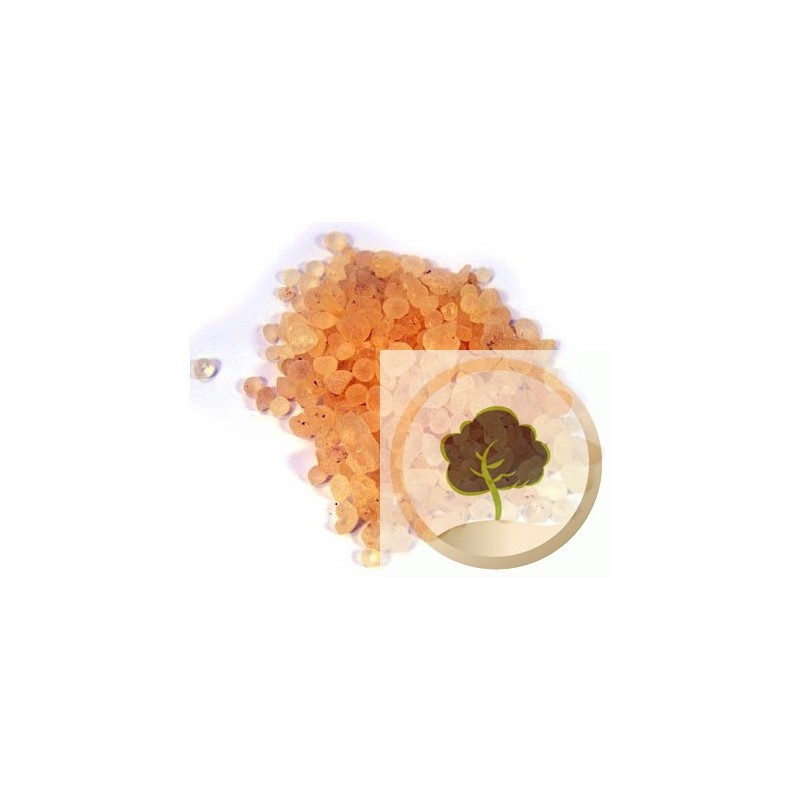







Gum arabic is a multi-functional hydrocolloid that features a highly branched arabino-galactan-protein complex , it can be used to boost fiber levels in a food or beverage without drastically altering the finished viscosity.
Net weight : 100 g
 Secure payment
Secure payment
You can pay securely
 Quick delivery
Quick delivery
We deliver your order directly after receipt of payment
 Satisfied or refunded
Satisfied or refunded
If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, simply return for refund
Gum Arabic
Origins of Gum Arabic :
Derived from the sap of the African acacia tree, gum arabic is one of the world’s most common gums with the longest history. Also known as gum acacia, it was used in ancient times for purposes as varied as mummification and inks for hieroglyphics. In 1949, TIC Gums added gum arabic to its growing line of tree exudates.

The Health Benefits of Gum Arabic
In addition to its functional properties, gum arabic plays an important dietary role. It is an excellent source of soluble dietary fiber (more than 85% on dry basis) and because of its low viscosity (300 cP maximum in a 1% solution), can be used to boost fiber levels in a food or beverage without drastically altering the finished viscosity. Learn more about the benefits of soluble dietary fiber from gums.
Gum Arabic: A Versatile Emulsifier
Gum arabic is a versatile hydrocolloid that has many applications. A superior emulsifier, our Gum Arabic Spray Dry Powder is widely used in the production of beverage and flavor emulsions and meal replacers. Its low viscosity and adhesive properties, meanwhile, make gum arabic an excellent ingredient for coating cereal, confections, and snack foods. For bakery products, the gum’s binding and emulsification abilities aid in the formulation of icings and frostings as well as baked goods like cakes and muffins.
Properties:
Gum Arabic is not toxic. Tasteless and odourless, it is soluble in water but not in alcohol.
Care :
Boiled Gum Arabic used to women after childbirth; to treat boils; for the treatment of diseases of the skin, wounds, leprosy, dysentery, etc. It is also used for excipient in the manufacture of some drugs.